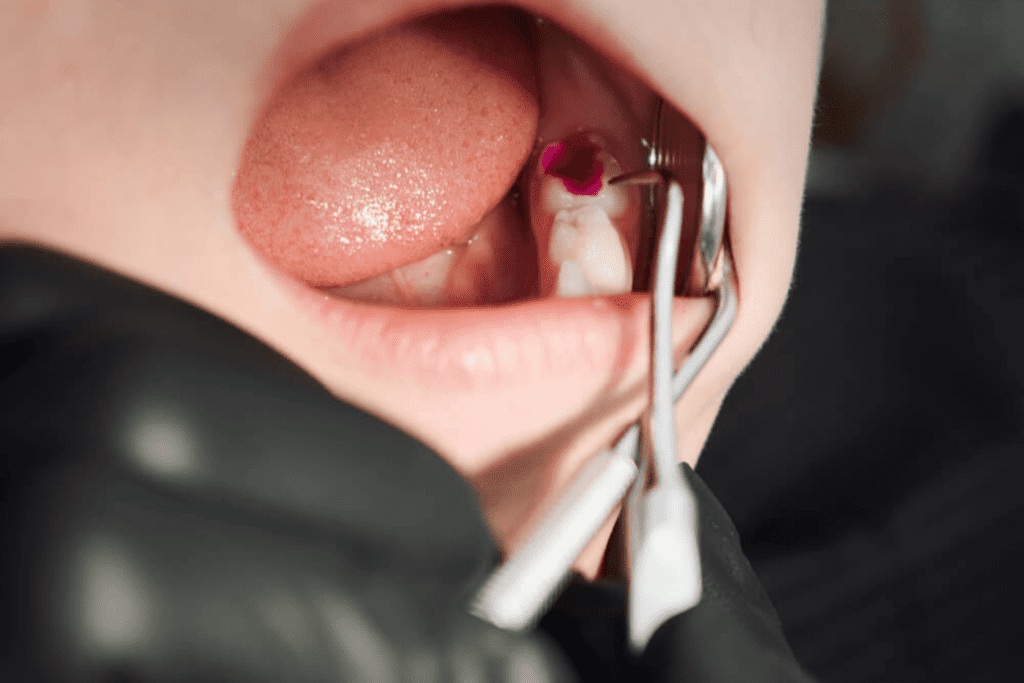
A tooth abscess is a painful infection that occurs at the root of a tooth or in the space between the tooth and the gums. It is usually caused by bacteria that enter the tooth through a cavity, crack, or chip in the tooth enamel. The bacteria can then spread to the root of the tooth and cause an infection.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe abscess forms as the body’s immune system tries to fight off the infection. Pus-a thick fluid containing dead tissue, bacteria, and white blood cells, accumulates in a pocket within the tooth or surrounding tissues. This can lead to intense pain, swelling, redness, and a throbbing sensation in the affected area.
Symptoms of a Tooth Abscess
The symptoms of a tooth abscess can vary in severity, but they generally include the following:
Severe Toothache
The most common symptom of a dental abscess is a persistent and throbbing toothache that may radiate to the jaw, ear, or neck. The pain is often intense and worsens with pressure or when biting or chewing.
Related: Tooth Pain (Toothache) Overview
Swelling
The area around the infected tooth or gums may become swollen, red, and tender to the touch. The swelling can be localized or spread to the surrounding tissues, causing a noticeable bulge.
Sensitivity
The affected tooth may become sensitive to hot or cold temperatures, causing pain or discomfort when consuming hot or cold foods or beverages.
Bad Taste and Breath
An unpleasant taste in the mouth, often described as bitter or salty, can be present due to the accumulation of pus and bacteria. This can also lead to persistent bad breath.
Fever
In some cases, a tooth abscess may cause a low-grade fever, typically indicating that the infection has spread beyond the immediate area of the tooth.
Difficulty Opening the Mouth
Swelling and inflammation associated with a tooth abscess can make it difficult to fully open the mouth, causing discomfort or pain when trying to eat or speak.
What Causes an Abscess Tooth
An abscessed tooth is primarily caused by a bacterial infection. The most common underlying causes of a tooth abscess include:
Tooth Decay
Cavities or dental caries occur when bacteria in the mouth produce acid that erodes the tooth enamel, leading to a cavity. If left untreated, the decay can progress and reach the tooth’s pulp, where the nerves and blood vessels are located. Bacteria can then infect the pulp, causing an abscess.
Gum Disease
Periodontal disease, such as gingivitis or periodontitis, involves inflammation and infection of the gums. If left untreated, the infection can spread from the gums to the root of the tooth, leading to an abscess.
Dental Trauma
A tooth that has suffered trauma, such as a crack, chip, or fracture, can create an entry point for bacteria to penetrate the tooth. This can result from a sports injury, accident, or biting down on a hard object.
Failed Dental Procedures
Sometimes, complications can arise from dental procedures such as fillings or root canals. If the tooth is not properly sealed or if bacteria enter the treated area, infection, and abscess can develop.
Weakened Immune System
Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with certain medical conditions or undergoing immunosuppressive treatments, may be more susceptible to tooth infections and abscesses.
Tooth Abscess Stages
Tooth abscesses can progress through different stages as the infection develops. The stages of a dental abscess typically include the following:
1. Initial Infection
The initial stage occurs when bacteria enter the teeth through a cavity, crack, or other opening. Bacteria begin to multiply and spread within the tooth or the surrounding tissues.
2. Inflammation and Swelling
As the infection progresses, the body’s immune response kicks in, resulting in inflammation and swelling in the affected area. This stage is characterized by redness, tenderness, and localized swelling of the gums or the face near the abscess.
3. Formation of an Abscess
The abscess begins to form as the body tries to isolate the infection. Pus-a thick fluid containing dead tissue, white blood cells, and bacteria, accumulates in a pocket or cavity. The abscess can be seen on dental X-rays or may be visible as a bump or pimple on the gums.
4. Increased Pain and Discomfort
As the abscess grows, the pressure within the affected area increases, leading to intensified pain and discomfort. The pain may become constant and severe, and it may radiate to other areas, such as the jaw, ear, or neck.
5. Spreading of Infection
If left untreated, the infection can spread beyond the initial site, affecting neighboring teeth, the jawbone, or even other parts of the body. This can lead to more serious complications and may require more extensive treatment.
Types of Dental Abscess
There are two main types of dental abscesses: periapical abscesses and periodontal abscesses.
Periapical Abscess
This type of abscess occurs at the tip of the tooth’s root, usually as a result of an infection spreading from the pulp of the tooth. It is commonly associated with tooth decay or dental trauma. The bacteria enter the teeth through a cavity or crack, infect the dental pulp, and then progress to the root, leading to an abscess. Periapical abscesses are typically characterized by localized pain, swelling, and a small pimple-like bump on the gum near the affected tooth.
Periodontal Abscess
This type of abscess forms in the supporting structures of the tooth, such as the gums and the periodontal ligament. It is usually caused by an infection that occurs in the space between the teeth and the gum (the periodontal pocket) due to gum disease or gum inflammation (gingivitis). Periodontal abscesses are often associated with poor oral hygiene, which allows bacteria to accumulate and cause an infection. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, redness, and the presence of pus between the tooth and gum.
It’s worth noting that there can be variations and overlap between these two types of abscesses. In some cases, a dental abscess may involve both the tooth’s root and the surrounding periodontal tissues.
Tooth Abscess Home Remedies
While home remedies cannot cure a dental abscess completely, they may help alleviate symptoms temporarily until you can see a dentist for proper treatment. It’s important to remember that these remedies should not replace professional dental care, as the infection needs to be properly treated to prevent further complications. Below are several home remedies that might offer some relief:
Saltwater Rinse
Mix half a teaspoon of salt in eight ounces of warm water until dissolved. Gently swish the solution in your mouth for about 30 seconds, focusing on the affected area. This can help reduce swelling and temporarily relieve pain.
Clove Oil
Clove oil contains a natural anesthetic called eugenol, which can help numb the area and reduce pain. Soak a cotton ball in clove oil and apply it to the affected tooth or gum area for temporary relief. Be sure to dilute the clove oil with a carrier oil, such as olive oil, as pure clove oil can be irritating to the tissues.
Cold Compress
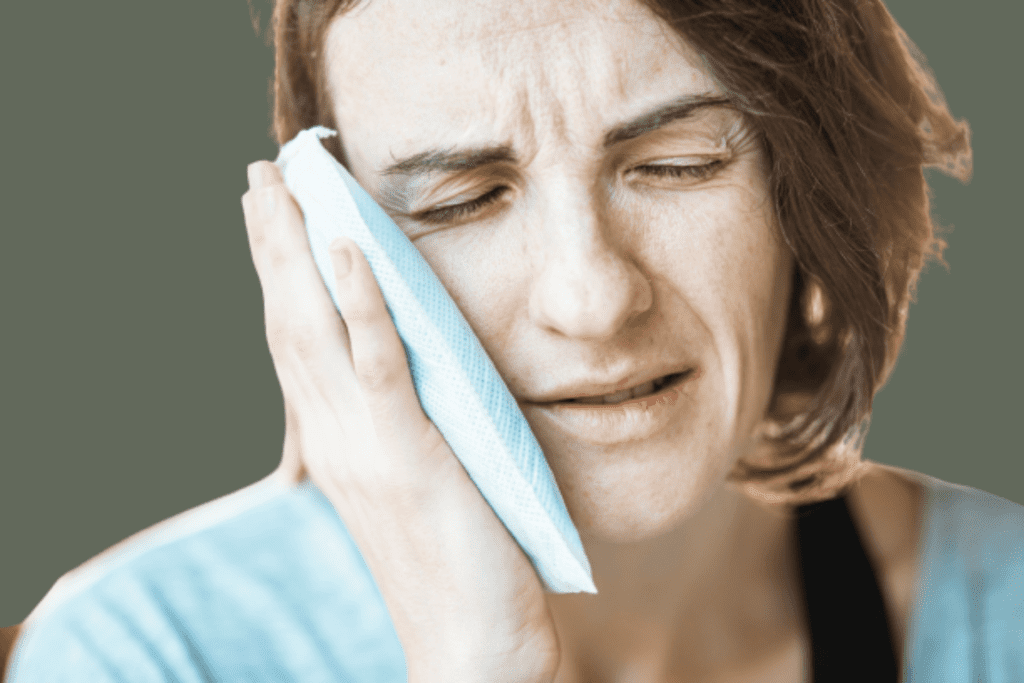

Applying a cold compress to the outside of your cheek near the affected area can help reduce swelling and provide some pain relief. Wrap a bag of ice or a cold pack in a thin cloth and apply it to the area for 15 minutes at a time.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Non-prescription pain medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Adhere to the directions provided on the packaging and seek advice from a healthcare professional if you have any concerns or medical conditions.
Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
Continue brushing your teeth gently and flossing, taking care to avoid the abscessed area. This can help prevent further infection and maintain overall oral health.
Tooth Abscess Treatment
The treatment of a tooth abscess typically involves a combination of dental procedures and medications. The specific treatment approach depends on the severity of the abscess and the underlying cause. It’s important to consult a dentist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Here are some common treatment options for tooth abscesses:
Drainage of the Abscess
When treating a dental abscess, one of the initial steps is to drain the abscess. The dentist will make a small incision in the abscess to allow the accumulated pus to be released. This not only provides immediate relief by reducing pressure and relieving pain but also helps in promoting the healing process.
Root Canal Therapy
If the infection has reached the tooth’s pulp, a root canal procedure may be necessary. During a root canal treatment, the dentist carefully removes the infected pulp from inside the tooth. Subsequently, the root canals undergo a process of cleaning, disinfection, and shaping. Afterward, a filling material is placed in the canals to seal them, preventing reinfection. In many cases, a dental crown is placed on the treated tooth to restore its strength and protect it from further damage.
Tooth Extraction
In certain situations, when the tooth is extensively damaged, cannot be saved, or the infection is too severe, extraction may be the recommended course of action. Tooth extraction involves the complete removal of the affected tooth from its socket. Following the extraction, your dentist may discuss options for tooth replacement, such as dental implants, bridges, or partial dentures, to restore the function and aesthetics of your smile.
Antibiotics
In some cases, antibiotics are prescribed to eliminate the infection and prevent its spread. Antibiotics are typically used when the infection has spread beyond the abscessed tooth, or when there are signs of systemic involvement, such as fever or swollen lymph nodes. However, it’s important to note that antibiotics alone cannot fully cure a tooth abscess, and they are usually used as an adjunct to dental procedures.
Pain Management
Pain management is an important aspect of tooth abscess treatment. Pain relief medications available without a prescription, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can assist in alleviating pain and decreasing inflammation. Your dentist may also prescribe stronger pain medications if necessary, depending on the severity of your symptoms. It’s important to follow the instructions provided by your dentist or pharmacist when taking pain medications.
Follow-Up Care
After undergoing treatment for a tooth abscess, it is crucial to follow your dentist’s instructions for post-treatment care. This may include taking any prescribed medications as directed, maintaining good oral hygiene practices (such as brushing and flossing regularly), and attending follow-up appointments. These follow-up visits allow your dentist to monitor the healing process, ensure the infection is fully resolved, and address any concerns that may arise.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a tooth abscess is a serious dental condition caused by a bacterial infection. It can lead to severe pain, swelling, and other symptoms. Home remedies may provide temporary relief, but they should not replace professional dental care. Seeking prompt treatment from a dentist is essential for proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Treatment options for a dental abscess may include drainage of the abscess, root canal therapy, tooth extraction, antibiotics, and pain management. Following the dentist’s instructions and attending follow-up appointments are crucial for proper healing and the prevention of further complications.
Remember, it is important to prioritize dental care and consult with a dental professional to ensure the best outcome for your oral health.
Resources
Image Designed by Freepik
References
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tooth-abscess/symptoms-causes/syc-20350901
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493149/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3623375/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dental_abscess
https://www.colgate.com/en-za/oral-health/adult-oral-care/4-home-remedies-for-abscessed-teeth
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tooth-abscess/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20350907