We sometimes add products that we believe may be beneficial to our readers. We may receive a small commission if you purchase using the links on this page. Read our affiliate disclaimer
List of Liver Diseases: The liver is a vital organ that plays a central role in various physiological processes, including metabolism, detoxification, and the production of essential proteins. However, it is susceptible to a wide range of diseases and syndromes that can have significant implications for overall health. In this article, we delve into an extensive list of 50 liver diseases and syndromes, exploring their characteristics, causes, symptoms, and potential treatments.
1. Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is an infectious liver disease caused by a virus. It is usually transmitted through contaminated food and water. Symptoms include fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), and dark urine. Most people recover fully without specific treatment.
2. Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that can lead to chronic liver disease. It spreads through contact with infected blood, sexual contact, or from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth. Symptoms are similar to hepatitis A, but some cases can progress to chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, or liver cancer.
3. Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral infection primarily transmitted through blood contact. It often leads to chronic liver disease and can cause severe liver damage over time. Many infected individuals remain asymptomatic for years until the disease has significantly advanced.
4. Cirrhosis
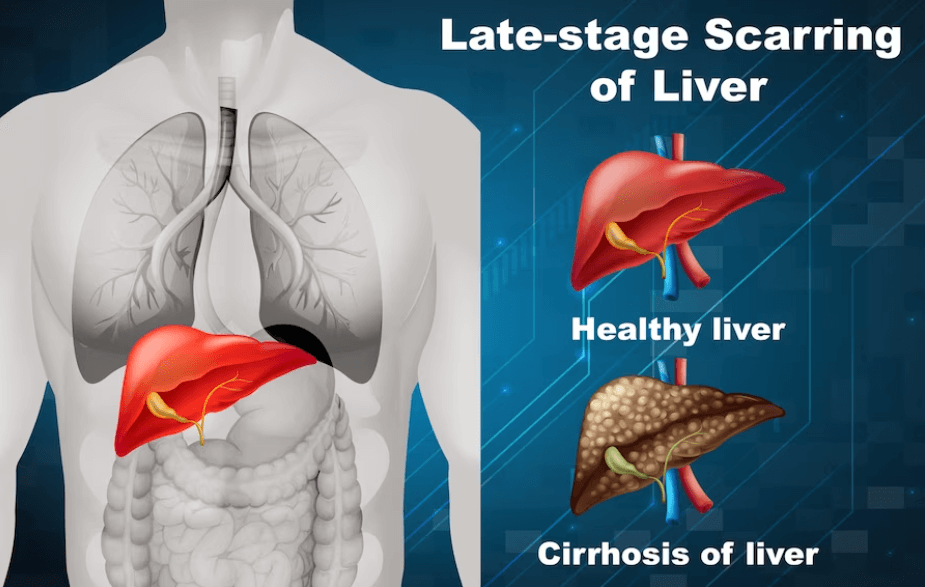
Cirrhosis is an advanced liver disease characterized by the replacement of healthy liver tissue with scar tissue. This scarring disrupts liver function, leading to symptoms like fatigue, jaundice, fluid buildup in the abdomen, and a higher risk of liver cancer. Cirrhosis is often a result of chronic liver diseases like hepatitis B, hepatitis C, or alcohol-related liver disease.
5. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a medical condition in which the liver accumulates excess fat, unrelated to excessive alcohol consumption. It exhibits a strong association with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. NAFLD encompasses a spectrum from simple fatty liver to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a more severe form that can lead to the development of cirrhosis.
6. Alcoholic Liver Disease
Alcoholic liver disease results from chronic alcohol consumption. It includes fatty liver (steatosis), alcoholic hepatitis (inflammation), and cirrhosis. Symptoms may include jaundice, abdominal pain, and liver enlargement.
7. Autoimmune Hepatitis
In autoimmune hepatitis, the body’s immune system attacks the liver cells, leading to inflammation and potential damage. The condition can be chronic or acute and may require immunosuppressive medications for management.
8. Hemochromatosis
Hemochromatosis is an inherited disorder causing excessive iron absorption from the diet, leading to iron buildup in the liver, pancreas, and other organs. Over time, this iron accumulation can lead to organ damage.
9. Wilson's Disease
Wilson’s disease is a genetic disorder that impairs copper metabolism, causing copper to accumulate in the liver and brain. This excess copper damages these organs, leading to liver disease and neurological symptoms.
10. Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
This genetic disorder affects the production of alpha-1 antitrypsin, a protein that protects the lungs and liver. A deficiency of this protein can lead to liver disease, lung disease, or both.
11. Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC)
PBC is an autoimmune condition where the small bile ducts in the liver are gradually destroyed, leading to bile buildup, liver inflammation, and scarring. It predominantly affects middle-aged women.
12. Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC)
PSC is an autoimmune disease causing inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts, which can lead to cirrhosis and liver failure. It is associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in many cases.
13. Budd-Chiari Syndrome
Budd-Chiari syndrome results from blood clot formation in the hepatic veins, which carry blood from the liver to the heart. This clotting obstructs blood flow from the liver, leading to liver enlargement and dysfunction.
14. Gilbert Syndrome
Gilbert syndrome is a benign genetic condition where the liver has difficulty processing bilirubin, leading to mild jaundice but no other liver abnormalities. It is usually harmless.
15. Drug-Induced Liver Injury
Certain medications, herbs, or supplements can cause liver damage in susceptible individuals. The severity can range from mild elevation in liver enzymes to acute liver failure.
16. Acute Liver Failure
Acute liver failure is a life-threatening condition where the liver rapidly loses its ability to function. It can be caused by viral infections (e.g., hepatitis A, B, or E), drug toxicity, or other factors.
17. Alagille Syndrome
Alagille syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects the liver’s bile ducts, heart, and other organs. Liver-related symptoms include cholestasis (impaired bile flow) and abnormalities in liver function tests.
18. Cholangiocarcinoma
Cholangiocarcinoma is a type of liver cancer that originates in the bile ducts. It can be challenging to diagnose and is often detected at advanced stages.
19. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
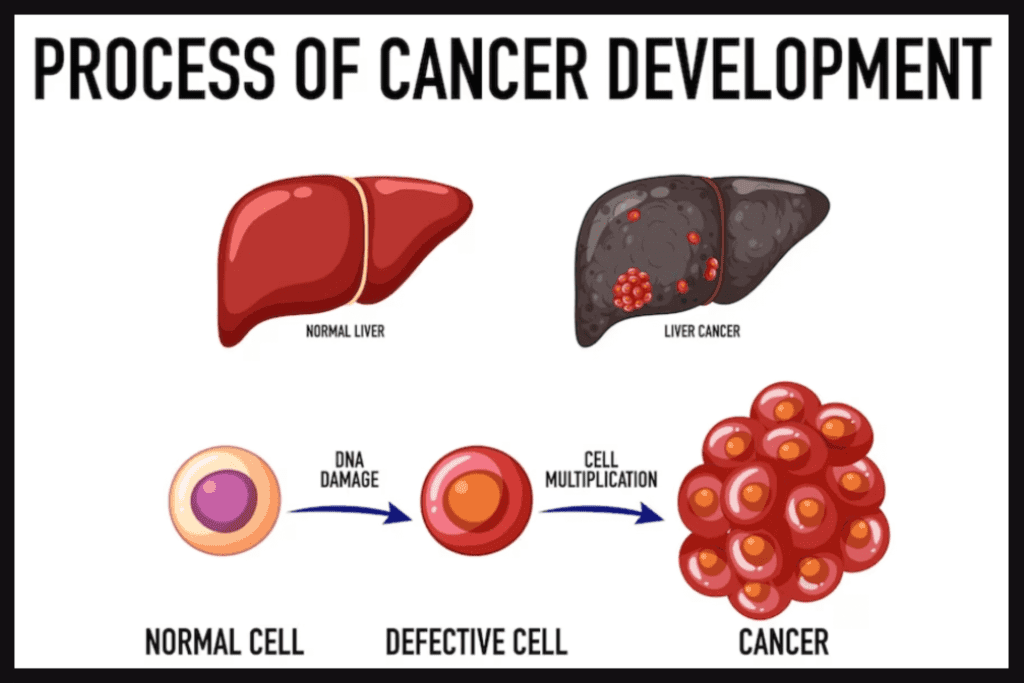
HCC is the most common form of liver cancer, arising from hepatocytes (liver cells). It is often associated with cirrhosis caused by chronic hepatitis B or C, alcohol-related liver disease, or NAFLD/NASH.
20. Hemangiosarcoma
Hemangiosarcoma is an uncommon form of liver cancer originating from the blood vessels within the liver. This aggressive tumor is associated with a bleak prognosis.
21. Biliary Atresia
Biliary atresia is a congenital condition where the bile ducts are blocked or absent, leading to bile flow obstruction. If not treated early, it can lead to cirrhosis and liver failure in infants.
22. Galactosemia
Galactosemia is a metabolic disorder that prevents the breakdown of galactose, a sugar found in milk. The buildup of galactose can lead to liver damage among other complications.
23. Glycogen Storage Diseases
Glycogen storage diseases are a group of inherited disorders affecting the liver’s ability to store and release glycogen, a form of glucose used for energy.
24. Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy is a condition where the liver’s impaired function leads to a buildup of toxic substances (ammonia) in the bloodstream, affecting the brain and causing neurological symptoms.
25. Hepatorenal Syndrome
Hepatorenal syndrome is a severe complication of advanced liver disease where the kidneys fail to function properly. It is associated with poor prognosis without liver transplantation.
26. Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy (ICP)
Polycystic liver disease is a condition where multiple cysts develop in the liver, leading to liver enlargement and potential complications.
28. Reye's Syndrome
Reye’s syndrome is a rare but severe condition that primarily affects children recovering from viral infections, particularly those who have taken aspirin. It causes liver and brain inflammation, leading to potentially life-threatening complications.
29. Secondary Liver Cancer
Secondary liver cancer occurs when cancer spreads (metastasizes) to the liver from other organs, such as the colon, breast, or lung.
30. Alpha-Fetoprotein Deficiency
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a protein produced by the developing fetus. AFP deficiency can be associated with liver and neurological issues in affected individuals.
31. Liver Abscess
A liver abscess is a collection of pus within the liver, often caused by bacterial infections that spread from other parts of the body or through the bile ducts.
32. Liver Cysts
Liver cysts are sacs filled with fluid that can develop within the liver. Most cysts are benign, but large or multiple cysts may cause symptoms or require treatment.
33. Liver Fibrosis
Liver fibrosis marks the initial phase of liver scarring, typically occurring as a consequence of chronic liver inflammation. If left unaddressed, this condition can advance to cirrhosis.
34. Liver Metastases
Liver metastases refer to cancerous tumors that originate from primary cancer sites in other parts of the body and have spread to the liver.
35. Hepatic Adenoma
Hepatic adenoma is a benign tumor that arises from liver cells. It is more common in women and may be associated with the use of oral contraceptives.
36. Hepatoblastoma
Hepatoblastoma is a rare form of liver cancer that primarily affects infants and young children. It is often curable with early diagnosis and treatment.
37. Liver Hemangioma
Liver hemangioma is a benign liver tumor composed of blood vessels. Most liver hemangiomas do not cause symptoms or require treatment
38. Liver Hydatid Cyst
A liver hydatid cyst develops due to the presence of the larval stage of the tapeworm Echinococcus. If not treated, it can result in liver damage and other potential complications.
39. Congenital Hepatic Fibrosis
Congenital hepatic fibrosis is a genetic disorder causing abnormal fibrous tissue growth in the liver and sometimes the kidneys.
40. Caroli Disease
FNH is a non-cancerous liver tumor characterized by abnormal blood vessels and hepatocytes. Most FNH cases are asymptomatic and do not require treatment.
42. Peliosis Hepatis
Peliosis hepatis is a rare condition where blood-filled cysts develop within the liver, potentially leading to liver enlargement and dysfunction.
43. Liver Trauma
Liver trauma occurs due to physical injury to the liver, often caused by accidents or blunt force.
44. Liver Hemangioendothelioma
Liver hemangioendothelioma is a rare vascular tumor that can occur in the liver. It can be benign or malignant and may require treatment depending on its size and location.
45. Liver Angiosarcoma
Liver angiosarcoma is a malignant tumor originating from the blood vessels in the liver. It is an aggressive cancer with a poor prognosis.
46. Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease (VOD)
VOD is a condition where the small veins in the liver become blocked, often due to certain medications or stem cell transplantation. It can lead to liver failure.
47. Liver Granuloma
Liver granulomas are small areas of inflamed tissue in the liver, often caused by infections like tuberculosis or autoimmune conditions.
48. Microscopic Liver Abscess
Microscopic liver abscesses are tiny abscesses in the liver, usually caused by bacterial infections.
49. Neonatal Hepatitis
Neonatal hepatitis is the inflammation of the liver that occurs in newborns, often attributed to infections, metabolic disorders, or autoimmune conditions. Depending on the cause and severity, it may resolve on its own or necessitate appropriate treatment.
50. Liver Infarction
Liver infarction is tissue death in the liver caused by inadequate blood supply, often associated with conditions like hepatic artery thrombosis or shock.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this comprehensive exploration of liver diseases and syndromes highlights the significance of the liver’s role in maintaining overall health. The list encompasses a wide array of conditions, from viral infections like hepatitis to genetic and metabolic disorders. The impact of liver diseases on individuals can range from mild symptoms to severe complications, including liver failure and cancer. While medical knowledge continues to evolve, understanding these conditions’ causes, symptoms, and available treatments is essential for early detection and management.
Read Next: Hepatitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Resources
Image Designed by Freepik
References
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554597/
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/liver-disease/cirrhosis
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/liver-disease/nafld-nash/definition-facts
https://medlineplus.gov/liverdiseases.html
https://dom.pitt.edu/gi/research/liver-diseases/
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/24/14/11758