We sometimes add products that we believe may be beneficial to our readers. We may receive a small commission if you purchase using the links on this page. Read our affiliate disclaimer
Brain fog is a term used to describe a condition characterized by cognitive difficulties, such as memory problems, difficulty concentrating, mental fatigue, and a lack of mental clarity. It is often associated with a sense of fogginess or cloudiness in thinking, leading to challenges in daily functioning and overall cognitive performance.
Table of Contents
ToggleIt is a common complaint among individuals of all ages and can significantly impact daily life.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the symptoms, causes, and potential treatment options for brain fog, shedding light on this often misunderstood condition.
Symptoms of Brain Fog
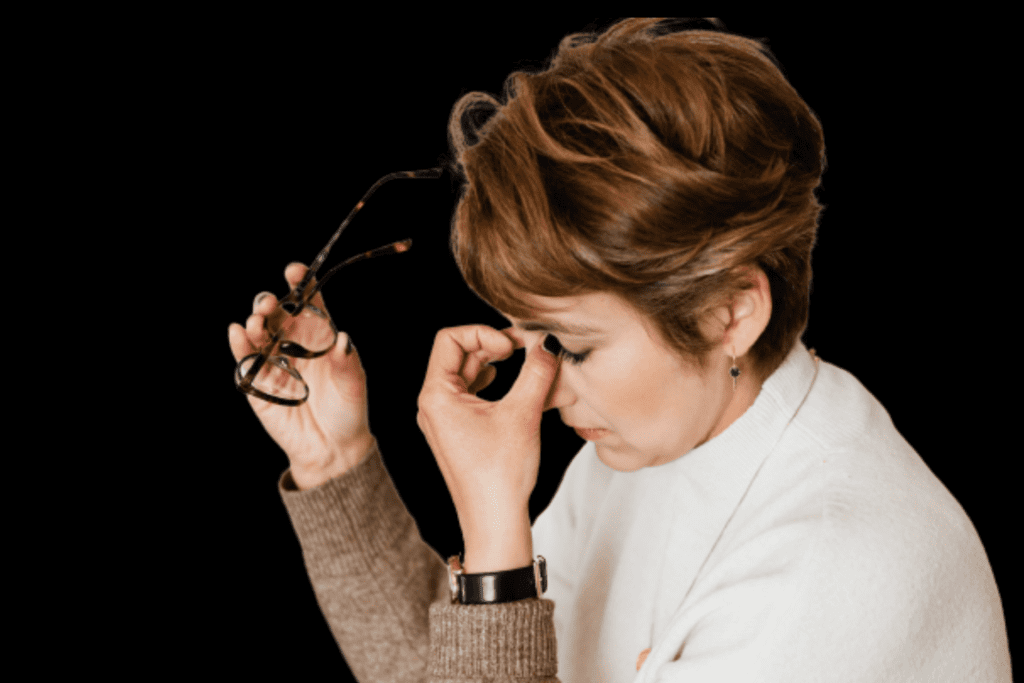

Brain fog manifests through a range of cognitive symptoms that can interfere with daily activities and overall cognitive performance.
Understanding these symptoms is essential for recognizing and addressing mental fog effectively.
Difficulty Concentrating
One of the primary symptoms of mental fog is the inability to concentrate or maintain focus. Individuals may find it challenging to complete tasks, stay engaged in conversations, or read and comprehend information. This difficulty in concentration can significantly impact work or academic performance.
Memory Problems
Mental fog often leads to memory difficulties, both short-term and long-term. Individuals may struggle to remember recent events, names, or details from conversations.
Forgetfulness and memory lapses can cause frustration and affect confidence in one’s cognitive abilities.
Mental Fatigue
Mental fog is often accompanied by a sense of mental exhaustion. Even after a good night’s sleep, individuals may wake up feeling tired and experience ongoing mental fatigue throughout the day. This persistent fatigue can affect productivity, motivation, and the ability to engage in daily activities.
Slowed Processing Speed
Brain fog can result in a slowed processing speed, making it difficult to think quickly or respond promptly to stimuli.
Individuals may experience delays in decision-making, have difficulty multitasking, or feel mentally sluggish. This can impact efficiency and overall cognitive performance.
Lack of Clarity
A common complaint among individuals with brain fog is a lack of mental clarity. Thoughts may feel muddled, and it can be challenging to articulate ideas or express oneself coherently. This can affect communication skills and interpersonal interactions.
Causes of Brain Fog
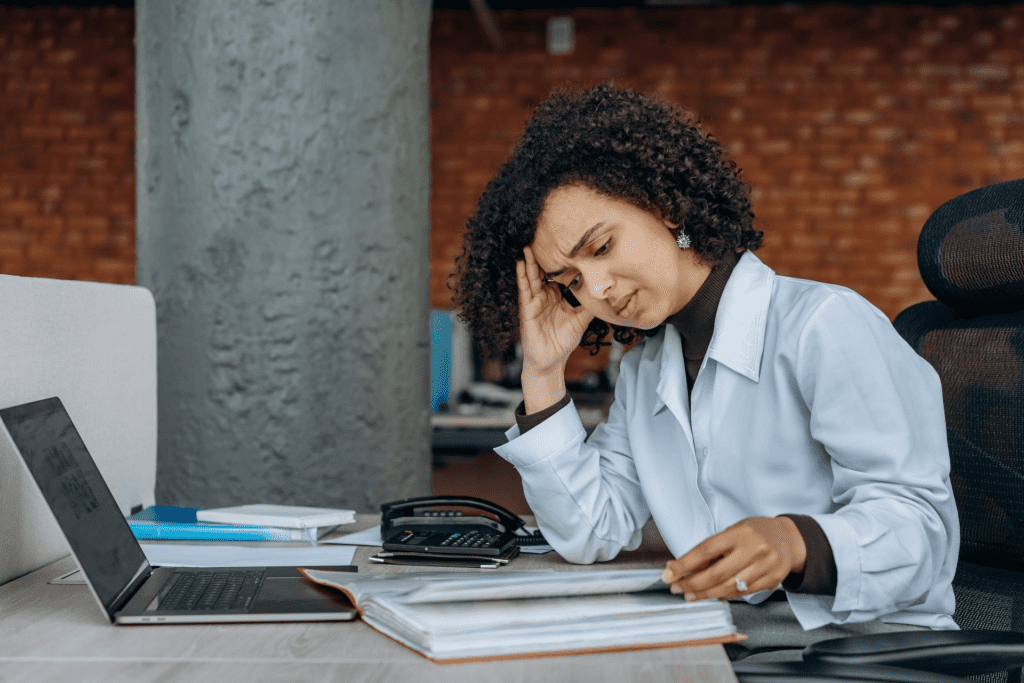

Mental fog can have various underlying causes, contributing to its development. Understanding these causes is crucial for determining appropriate treatment approaches and addressing the factors that contribute to mental fog.
Sleep Deprivation
Inadequate sleep or poor sleep quality can impair cognitive function and contribute to brain fog. During sleep, the brain consolidates memories, removes toxins, and restores cognitive function.
Lack of sleep can lead to impaired cognitive abilities, decreased attention span, and difficulties with memory and focus.
Stress and Anxiety
High levels of stress and anxiety can have a profound impact on cognitive function and contribute to brain fog.
Chronic stress triggers the release of stress hormones, such as cortisol, which can disrupt neurotransmitter balance and impair cognitive processes.
Anxiety can lead to racing thoughts, difficulty concentrating, and mental exhaustion.
Nutritional Deficiencies
A well-balanced diet is crucial for optimal brain function, and nutritional deficiencies can contribute to mental fog.
Deficiencies in essential nutrients like vitamins B12, D, and omega-3 fatty acids can impair cognitive abilities and contribute to brain fog.
Vitamin B12, in particular, is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system and the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen to the brain.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, such as those experienced during menopause, pregnancy, or thyroid imbalances, can contribute to mental fog.
Changes in estrogen and progesterone levels can affect neurotransmitter function, leading to cognitive difficulties, mood changes, and memory problems.
Thyroid imbalances can also disrupt cognitive function and contribute to brain fog.
Chronic Health Conditions
Mental fog can be a symptom of various chronic health conditions, such as fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, autoimmune diseases, and Lyme disease.
These conditions can directly affect cognitive function and lead to brain fog as a result of inflammation, immune system dysregulation, or neurochemical imbalances.
It’s important to recognize and address the underlying health conditions to effectively manage brain fog symptoms.
Treatment of Brain Fog
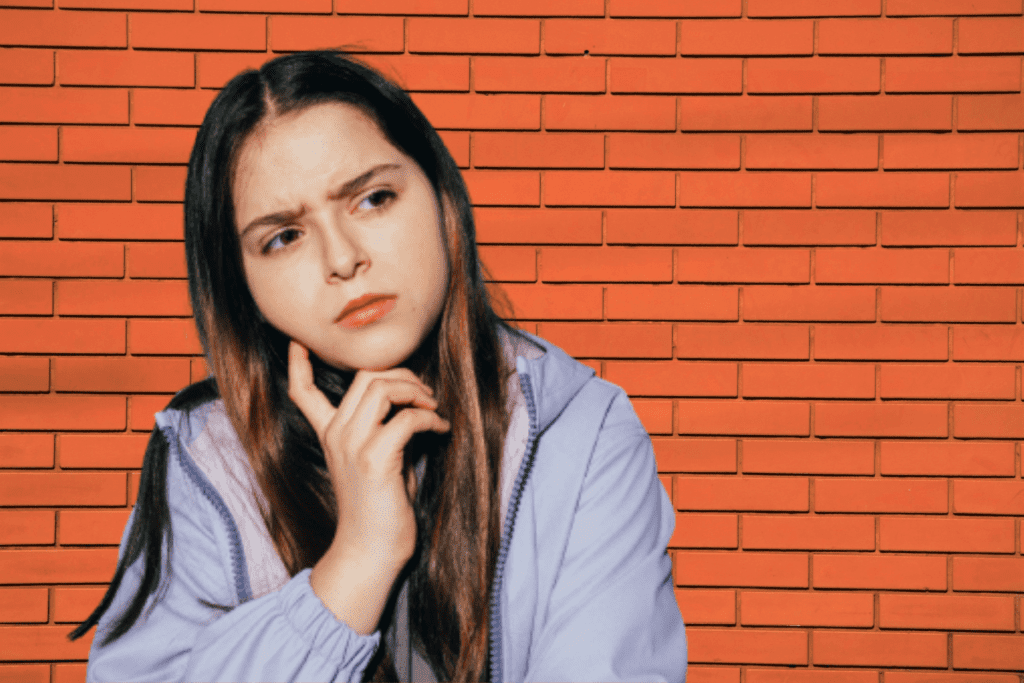

Managing brain fog involves addressing the underlying causes and implementing strategies to improve cognitive function and mental clarity. Here are some potential treatment options for mental fog:
Adequate Sleep
Prioritizing a good night’s sleep is critical for preventing brain fog. Create a sleep-friendly environment and a consistent sleep schedule.
This involves having a comfortable mattress, a dark and quiet room, and a pleasant nighttime routine. Avoiding stimulating activities before night, such as utilizing electronic devices, is also vital.
Aim for 7-9 hours of unbroken sleep each night to promote normal brain function and prevent symptoms of mental fog.
Stress Management
Effectively managing stress is vital for alleviating mental fog. Incorporate stress-reduction techniques into your daily routine, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, mindfulness, or engaging in activities you enjoy.
Regular exercise, such as yoga or aerobic activities, can also help reduce stress levels and improve cognitive function.
Related: Manage Stress – EFT Tapping (Emotional Freedom Technique): How Does it Work?
Balanced Diet
A nutrient-dense diet is important for maintaining brain function and decreasing mental fog. Consume whole foods such as fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Make sure you get enough vitamins and minerals, including B12, D, and omega-3 fatty acids. These nutrients are critical for brain function and can be supplied through food or supplementation if necessary.
Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity has numerous benefits for both physical and mental well-being. Exercise increases blood flow to the brain, promoting the delivery of oxygen and nutrients necessary for optimal cognitive function.
Aim for at least 150 minutes per week of moderate-intensity activity, such as brisk walking, running, cycling, or swimming.
Cognitive Stimulation
Keeping the brain active and engaged is crucial for improving cognitive function and reducing brain fog. Engage in activities that challenge your mind, such as puzzles, reading, learning a new instrument or language, or engaging in brain-training exercises. This stimulates neural connections and promotes mental agility.
Medication
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to alleviate mental fog symptoms. Stimulant medications, such as Ritalin or Modafinil, can improve alertness and concentration in individuals with severe brain fog. However, these medications should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare practitioner.
Therapy
Counseling or therapy may be beneficial for individuals experiencing mental fog due to underlying psychological factors. Therapists can help individuals manage stress, anxiety, or depression, which can contribute to cognitive difficulties. They may provide coping strategies, relaxation techniques, or cognitive-behavioral therapy to improve overall mental well-being.
Treatment of Underlying Health Conditions
If mental fog is a symptom of an underlying health condition, treating the root cause is essential for reducing symptoms. Consult with a healthcare professional to diagnose and manage any chronic conditions contributing to brain fog. This may involve medications, lifestyle changes, or other interventions specific to the underlying condition.
Conclusion
Brain fog can significantly impact daily life and overall well-being, but it is a treatable condition. By recognizing the symptoms, understanding the potential causes, and implementing appropriate treatment strategies, individuals can alleviate brain fog symptoms and improve cognitive function.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan tailored to individual needs. With the right approach, it is possible to overcome brain fog and regain mental clarity.
Read next: What is Stress: How to Manage It?
References
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36600580/#:~:text=Conclusions%3A%20’Brain%20fog’%20is,of%20illnesses%2C%20drugs%20and%20behaviours.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23999934/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1530891X21014087
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5579396/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547676/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25583051/
https://www.healthline.com/health/chronic-fatigue-syndrome